HousePlantJoy is supported by our audience. When you purchase through one of our links, we may earn a small affiliate commission. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases. Your cost is not affected.
==================
Is it time to plant your garden? It may feel like spring, but knowing minimum winter temperatures in your USA gardening zones provides the best information for when to plant. Plant too soon and your crops might suffer a spring freeze. Too late, and they might not be ready for harvesting before the fall temperatures drop.
Choosing the Right Plants for Your Region: A Look at the USA Gardening Zones
Even those in the southern climates with the USA gardening zones of 8, 9, or 10 need to know this information. For these zones, the problem often reverses. However, southern gardeners often benefit from having two growing seasons for many vegetables.
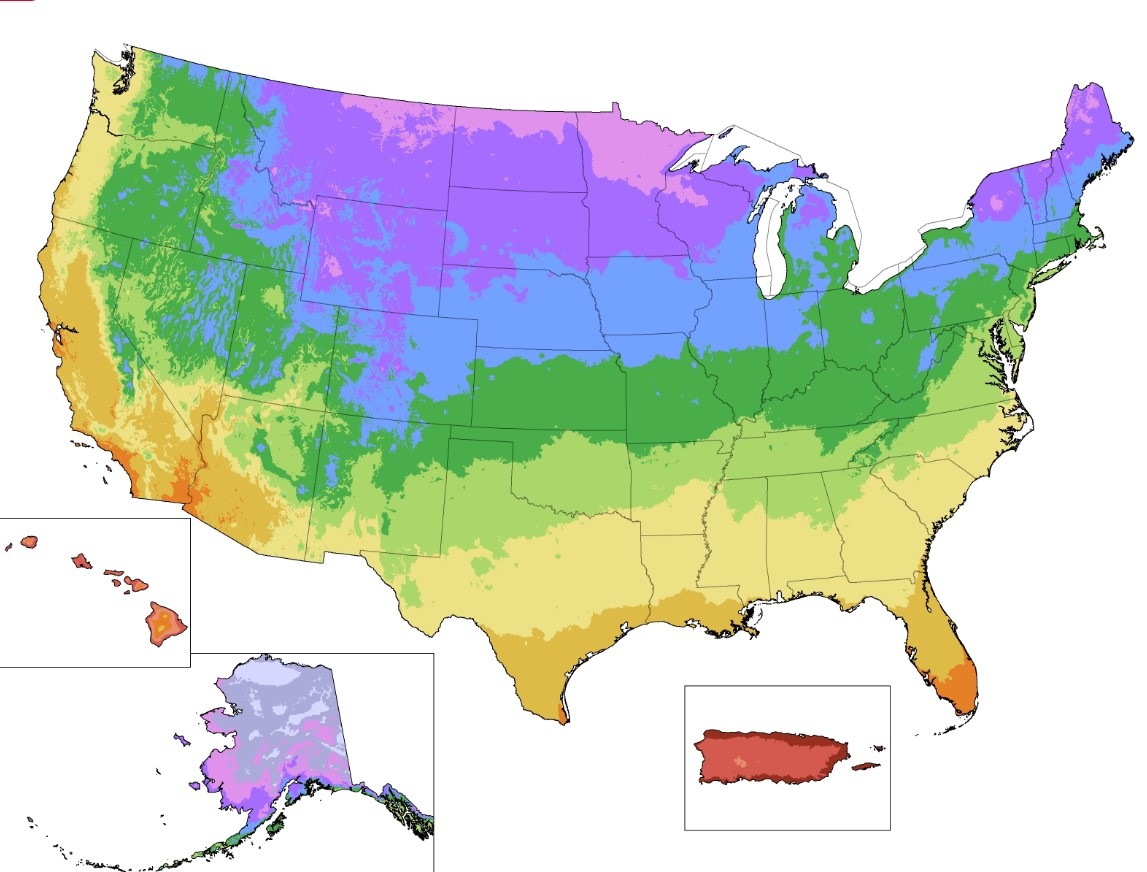
Learn About USDA Hardiness Zones
Image Source: Pexels
As a passionate gardener, I have always been fascinated by the diversity of plants that can be grown in different regions of the United States. However, I have also learned that not all plants are suitable for all regions, and choosing the right plants for your garden can make all the difference in the success of your gardening efforts. In this article, I will guide you through the different gardening zones in the USA and provide you with tips on how to choose the right plants for your region.
Understanding the Different Gardening Zones in the USA
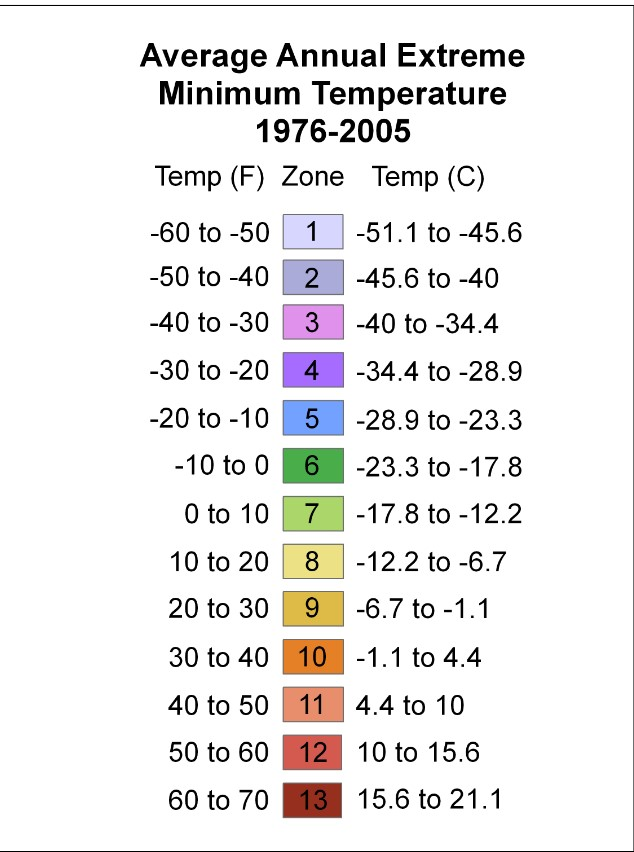
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has divided the country into 13 different hardiness zones based on the average annual minimum temperature in each area. These zones range from the coldest hardiness zone number 1 in Alaska, where temperatures can drop as low as -60°F, to the warmest zone 13 in Puerto Rico, where temperatures rarely fall below 60°F. Each gardening zone is further divided into subzones based on the length of the growing season, the average temperature, and other climatic factors that affect plant growth.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Plants for Your Region
When choosing plants for your garden, it is important to take into account the specific conditions of your gardening zone. Some of the factors to consider include:
Number of Growing Days vs Freeze Days
The hardiness zone maps help provide the growing days gardeners should expect. They also take into account the freeze times, frost, and temperatures. Generally speaking, the further south you go, the longer your growing season.
However, the southern states experience two separate growing zones for many crops. Cooler weather crops might flourish in the fall and again in late winter to early spring.
Another factor that ties in with the freeze times is the last frost date. This is the estimated date that the area might experience the last freeze. While the hardiness zone might give an actual date, such as April 15, keep in mind that this last frost date is an estimate. That last freeze can happen days or even weeks later in some years.
Temperature
Photo by Ilse Orsel on Unsplash
Plants have different temperature requirements, and choosing plants that are adapted to your gardening zone will ensure that they thrive in your garden. For example, plants that are adapted to cold climates will not do well in warm regions, and vice versa.
This map ties in with the hardiness zone maps. While 70°F might be common in zone 9 in February, zone 5 might not experience temperatures in the 70’s until Spring or summer.
Sunlight
Most plants require a certain amount of sunlight to grow and produce flowers or fruit. Knowing the amount of sunlight your garden receives throughout the day will help you choose plants that are suited to the light conditions of your garden.
Keep in mind that the location of your garden on your land also affects the amount of sunlight. Most vegetables and fruit plants grow best with a certain amount of sunlight. Some need more than others.
To ensure that the plants receive enough sunlight, most gardeners plan the garden area in a sunny location. Trees and bushes block out sunlight and interfere with plant growth.
Soil Type
Different plants grow best in different types of soil. Some plants prefer well-drained, sandy soils, while others thrive in heavy, clay soils. Testing your soil and choosing plants that are adapted to your soil type will help ensure that your garden thrives.
Basic test kits available online include the MySoil PRO pack and the Luster Leaf 1663 Professional Soil Kit. Alternatively, your local cooperative extension agent might offer help with soil testing for your local area.
If your soil needs adjusting, it’s easier to do before the first planting dates. Even native species benefit from adding fertilizers or other amendments to the soil if needed.
Water
Water is essential for plant growth, but different plants have different water requirements. Choosing plants that are adapted to your region’s rainfall patterns and soil moisture levels will help ensure that your garden is healthy and productive.
In addition, if you plan to water plants when needed, consider the location of your garden. Garden hoses help reach further areas of your property but plan for these when staking out the location.
Benefits of Planting According to Your Region’s Gardening Zone
One of the main benefits of planting according to your region’s gardening zone is that it increases the chances of success in your garden. Plants adapted to your region’s climate are more likely to thrive and produce a healthy crop. Additionally, planting according to your gardening zone can save you time and money by reducing the need for fertilizers, pesticides, and other inputs that are required to grow plants outside of their natural range.
Another benefit of planting according to your gardening zone is that it can help you conserve water. Plants that are adapted to your region’s climate are more likely to be drought-tolerant and require less water than plants that are not adapted to your region’s climate. This can help you save water and reduce your water bill.
Common Challenges When Planting Outside of Your Gardening Zone
While it is possible to grow plants outside of your gardening zone, there are several challenges that you may encounter. Plants that are not adapted to your region’s climate are more likely to suffer from stress, disease, and pest problems. Additionally, these plants may require more inputs, such as fertilizer and water, to grow and produce a healthy crop. This can be time-consuming and expensive.
Want to Beat the Hardiness Zone Maps?
Indoor garden systems, usually using hydroponic methods, such as this one by Gardyn, make indoor gardening not only possible but fun. While it does take longer to reach the break-even point of the system purchase, most people find that having excellent quality produce available year-round is worth the upfront investment.
While these systems show well in almost any room, you might consider turning a spare bedroom or a sun porch into a growing area indoors. This makes it easier to control the temperature, humidity, and actual climate that your plants grow. We find that plants grown this way over those planted in the ground often survive better, even when the outside weather is not good.
Another benefit to these year-round growing systems is that plants grown hydroponically in them usually mature more quickly and with few to no pests compared to those in the garden. More than just surviving, hydroponically grown plants usually thrive.
Another alternative to growing plants in the ground using soil is using a greenhouse. Hydroponics work well for this type of growing, too. A greenhouse extends your growing season, allowing you to plant earlier in the spring and continue later into the fall months.
Using a Planting Calendar to Plan Your Garden
A planting calendar is a useful tool for planning your garden and choosing the right plants for your gardening zone. A planting calendar will tell you when to plant different types of plants, vegetables, fruits, and flowers based on your region’s climate and growing season. This can help you maximize your garden’s productivity and ensure that you have a steady supply of fresh produce throughout the growing season.
Tip: Use the USDA hardiness zones map and information to help determine the best planting dates. Even if you have checked your planting zones before, it’s best to recheck. Yale University reports recent changes have been made due to the changes in temperature and climate. For more information on these changes, visit Climate.gov.
Top Plants for Each Gardening Zone in the USA
While some plants grow well in any zone, many require specific temperatures and lengths of the growing season. For instance, spinach grows quickly and be grown almost anywhere if you take into account your growing season. Oranges and other citrus, however, must be grown in warmer climates that seldom freeze.
For this reason, you must understand your growing zone which includes your last freeze date (estimated) and the average temperature of each month. Spinach may grow well in February in Zone 9 but won’t do as well in July in Zone 9 with the higher average temperatures. Likewise, spinach plants grow well in the summer in Zone 5 but won’t live long in the harsh cold of Zone 5. January freezes.
If in doubt, consult your local cooperative extension office. They provide free information on growing times, plants that perform best, and even how to manage pests. Also, they may have Master Gardeners available to assist you even further.
Resources for Finding the Best Plants for Your Region
There are many resources available to help you choose the best plants for your gardening zone. Some of these resources include:
- The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
- Old Farmer’s Almanac
- Local gardening clubs and associations
- Cooperative Extension Services
- Seed catalogs and nurseries
- Arbor day foundation
Tips for Successful Planting in Your Gardening Zone
Here are some tips for successful planting in your gardening zone:
- Choose plants that are adapted to your region’s climate and soil type
- Test your soil before planting to ensure that it has the right pH and nutrient levels
- Water your plants regularly, especially during dry periods
- Mulch your garden to conserve moisture and suppress weeds
- Rotate plant crops each year to reduce the possible risk of pests and other problems.
- Use organic fertilizers and pest control methods to reduce the use of synthetic chemicals
How to Make the Most of Your Region’s Gardening Zone
Choosing the right plants for your region’s gardening zone is key to a successful garden. By understanding the specific conditions of your gardening and planting zone and choosing plants that are adapted to these conditions, you can maximize your garden’s productivity and reduce the need for inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides.
Using a planting calendar and taking advantage of resources such as the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map and local gardening clubs can help you choose the best plants for your region. By following these tips and planting according to your gardening zone, you can create a healthy, productive garden that will provide you with fresh produce throughout the growing season.
FAQs on USA Gardening Zones
What Are USA Gardening Zones?
Gardening zones, also known as USDA Hardiness Zones, are geographical regions defined based on average minimum winter temperatures. These zones help gardeners determine which plants are most likely to thrive in their specific climate.
How Are Gardening Zones Determined?
The USDA Hardiness Zones are determined based on the average annual minimum winter temperature. The country is divided into zones, each representing a 10°F temperature range. The zones range from 1a (coldest) to 13b (warmest).
Where Can I Find My Gardening Zone?
You can find your gardening zone by checking the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, which is available online. Many gardening websites and plant catalogs also provide zone information for specific plant varieties.
Why Is It Important to Know My Gardening Zone?
Knowing your gardening zone is crucial for selecting plants that can withstand the winter temperatures in your area. It helps you choose plants that are well-suited to your climate, increasing the likelihood of successful gardening.
Follow Our Socials
Dive into the greenery on our Instagram, where we share captivating photos of vibrant houseplants and tips on how to keep them thriving. Connect with fellow plant enthusiasts on Twitter to discuss all things leafy and discover new varieties to add to your indoor jungle. Looking for inspiration on how to arrange your plants or create your oasis at home?
Explore our Pinterest boards for stunning visuals and creative ideas. Join our Facebook community for a friendly space to exchange advice, troubleshoot plant woes, and showcase your plant havens. Follow us across all platforms for a joyful and green adventure! #HousePlantJoy #PlantParenthood #GreenHomeHappiness